| 全基因组测序揭示了野生大角羊自然选择和性选择的分子标记 |
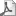
|
|
| 编辑: 贺善云 2015-10-14 | |
|
影响健康的基因的鉴定是我们理解适应性的遗传基础和野生种群的表型变异如何形成的核心。在一研究中,研究人员用> 50倍覆盖率的野生落基山大角羊(Ovis canadensis)全基因组测序确定280万个单核苷酸多态性和定向选择的基因组区域(即,选择性扫描)。通过X染色体和常染色体之间SNP多样性的比较表明,大角羊雄性与雌性相比,长期有效群体规模大幅减少。这可能反映了强烈的性选择介导的雄性间竞争配偶的悠久的历史。 选择性扫描基于杂合度和核苷酸多样性揭示的选择性扫描的证据发现其跨多个种群共享RXFP2,强烈地影响着国内的有蹄动物角的大小。大角公羊所携带巨大的角部分进化似乎是通过RXFP2并受到强烈正选择。研究人员发现确定的证据表明了个别群体中的基因的选择影响早期的身体生长和细胞对缺氧的反应;然而,这些必须得到更谨慎地解释因为遗传漂变在当地种群中很强烈并且可能造成假阳性。研究结果代表了一个罕见的例子即已知功能的基因在野生种群的非模型物种的选择强的基因组特征。此外研究结果还展示了密切相关的野生物种适应性的基因组基础研究的农业或模型物种参考基因组组件的值。 原文摘要如下: Whole genome resequencing uncovers molecular signatures of natural and sexual selection in wild bighorn sheep Kardos M1,2, Luikart G1,3, Bunch R4, Dewey S5, Edwards W6, McWilliam S4, Stephenson J5, Allendorf FW1, Hogg JT7, Kijas J4 Abstract: The identification of genes influencing fitness is central to our understanding of the genetic basis of adaptation and how it shapes phenotypic variation in wild populations. Here, we used whole genome resequencing of wild Rocky Mountain bighorn sheep (Ovis canadensis) to > 50 fold coverage to identify 2.8 million SNPs and genomic regions bearing signatures of directional selection (i.e., selective sweeps). A comparison of SNP diversity between the X chromosome and the autosomes indicated that bighorn males had a dramatically reduced long term effective population size compared to females. This likely reflects a long history of intense sexual selection mediated by male-male competition for mates. Selective sweep scans based on heterozygosity and nucleotide diversity revealed evidence for a selective sweep shared across multiple populations at RXFP2, a gene that strongly affects horn size in domestic ungulates. The massive horns carried by bighorn rams appear to have evolved in part via strong positive selection at RXFP2. We identified evidence for selection within individual populations at genes affecting early body growth and cellular response to hypoxia; however these must be interpreted more cautiously as genetic drift is strong within local populations and may have caused false positives. These results represent a rare example of strong genomic signatures of selection identified at genes with known function in wild populations of a non-model species. Our results also showcase the value of reference genome assemblies from agricultural or model species for studies of the genomic basis of adaptation in closely related wild taxa. Keywords: Ovis Canadensis, adaptation, coalescent simulations, effective population size, fitness; population genomics, selective sweeps 相关信息: |
|
| < 上一篇 | 下一篇 > |
|---|








